
Pull of the tendon results in a signal to the spinal cord along the afferent The stretch of the muscle in response to the Tapping on the knee pulls on the tendon of the extensor muscle thatĮxtends the lower leg. The simplest form of movement in response to sensation is Motor control, such as the face and hands, occupy a disproportionately Parts of the body that have acute sensation or fine Somatosensory and somatomotor gyrus of the cerebralĬortex is possible.

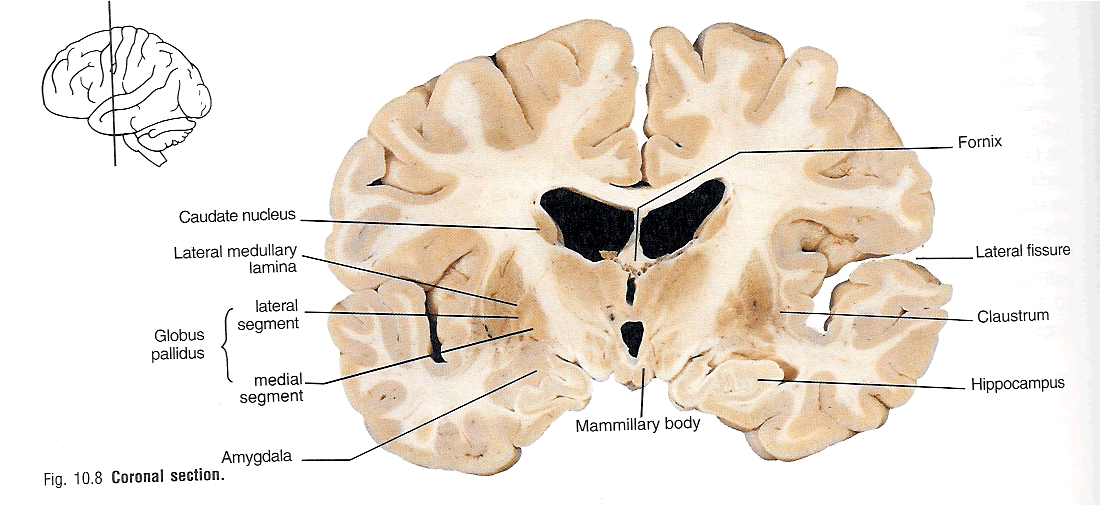
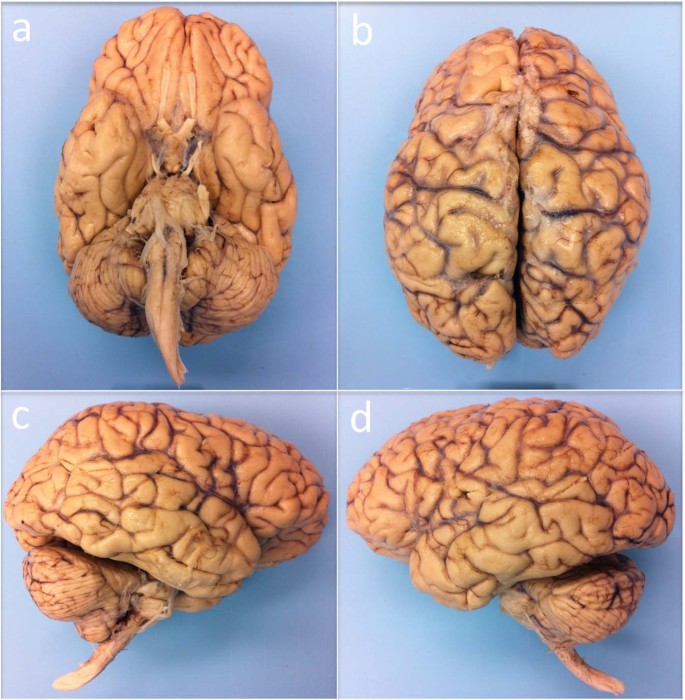
Precise localization of the body parts supplied by both the The precentral gyrus from the postcentral gyrus. Movement) to the body,ie, muscle control. Rearmost portion of the frontal lobe (the precentral gyrus) isĬoncerned with conveying motor information (initiation of voluntary Sensory information from the body - somatosensory information). The parietal lobe (the postcentral gyrus) is concerned with representing Processing sensory information from the nose. Input from the ears, and a portion of the frontal lobe is devoted to Whereas a portion of the temporal lobe is devoted to processing sensory Much of the occipital lobe is devoted to processing sensory input from the eyes The exterior of the cerebral cortex is divided into four lobes:įrontal, parietal, temporal and occipital. Ridge) is called a gyrus, whereas a "valley" between worms is called The cerebralĬortex has the appearance of a ball of worms. Well as muscle tension and movement information).Ĭortex, which is often regarded as the seat of the mind. Tracts: for crude touch, for pain&temperature, for motor control,Īnd for proprioception&kinesthesia (muscle, tendon & joint position as The spinal cord axons ascend-from and descend-to the brain in well-segregated Right side of the body are in the left brain, and vice versa. Axons in these nerves tend to cross to the Sensory information is mostly somatosensory: touch, temperature, pressureĪnd pain ("somato" = "body"). The spinal cord and its nerves are divided into four regions:Ĭervical (neck), thoracic (chest), lumbar (loin) and sacral Pairs of nerves receiving sensory information and sending motor information The spinal cord is housed in the backbone, with 30 The central nervous system (CNS), consists of the spinalĬord and the brain. The autonomic nervous system is a functionalĭivision of the nervous system which is part of both the CNS and the PNS. Portions: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral Whereas sympathetic stimulation increases heart rate, constrictsīlood vessels and decreases peristalsis in the intestine, parasympatheticĪnatomically, the human nervous system is divided into two The twoĭivisions of the autonomic nervous system are the sympathetic ("fight orįlight") and the parasympathetic ("rest and digest"). The kidneys, intestines, lungs, glands,īlood vessels, heart muscle, etc. are under the control of the ANS. Nervous system (ANS), a system that is (for the most part) not subject The internal environment is primarily the domain of the autonomic Motor activity in the internalĮnvironment can assist the ingestion of water until sensory informationįrom the internal environment provides evidence that enough water has Motor activity directed to the external environment can
Hippocampus anatomy gross how to#
Sensory input from theĮxternal environment provides that person with information on how to Provides a person with an awareness of thirst. For example, sensory input from the internal environment Motor output are relevant for both an internal and an externalĮnvironment. Viewed as a whole, the human nervous system is primarilyĬoncerned with the processing of sensory input or with theĮxecution of motor output (physical action).
SENSORY AND MOTOR AREAS OF THE CEREBRAL CORTEX.GROSS NEURO-ANATOMY Chapter 2 - Gross Neuro-Anatomy


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
